Demystifying DNS - Everything You Need to Know
Learn about DNS hierarchy, types, records, propagation, caching, security, and load balancing.
The article’s objective is to cover all the key information about the Domain Name System (DNS). Everyone interested in learning more about DNS should read this article. I will try to explain what you need to know in layman’s terms. Without further ado, let’s get into it.
What is DNS and why is it important?
DNS is like a big phone book for the internet. You know how you have a phone book at home with all your friends’ phone numbers and addresses? Well, DNS is like that, but for websites.
When you want to go to a website, you type in the website’s name, like “google.com". DNS takes that name and looks it up in the phone book to find the website’s “phone number”, which is called an IP address. Then, DNS tells your computer the IP address, and your computer uses that to find the website and show it to you.
DNS is essential because it helps us find websites easily and quickly, without having to remember a bunch of numbers. It’s like having an astute helper who knows where all the websites are and how to get to them!
What is the hierarchy of DNS?
Remember how I explained that DNS is like a big phone book for the internet? Well, it’s not just one big phone book. It’s actually lots of phone books, all working together in a big chain.
At the very top of the chain is something called the “root” server. This server lists all the top-level domains (TLDs), like .com, .org, .net, and so on.
When you type in a website name, like “google.com", your computer goes to the next level of the chain, which is the server for the “.com” top-level domain. That server has a list of all the websites that end in “.com”, and it can tell your computer where to find “google.com".
Then, your computer goes to the next level of the chain, which is the server for “google.com". That server has a list of all the pages on the Google website, and it can tell your computer where to find the page you’re looking for.
This chain of servers is called the “DNS hierarchy”, and it helps your computer find the right website quickly and easily. It’s like a big team of helpers, each one passing along the information to the next one until you get to where you want to go.
Here is a simple diagram of the DNS hierarchy for you to get an idea.
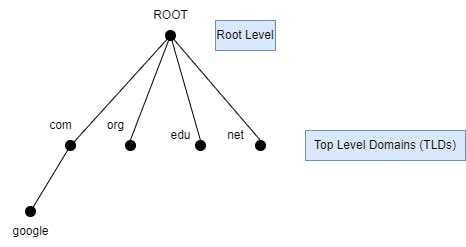
So, that’s how DNS hierarchy works! It’s a big chain of servers, each one responsible for a different part of the internet phone book, all working together to help us find websites.
What are the DNS server types?
DNS servers are like special computers that help to make the internet work. There are two main types of DNS servers.
authoritative DNS servers
recursive DNS servers
An authoritative DNS server is like a phone book for the internet. It stores information about domain names and their corresponding IP addresses. When someone wants to visit a website, their computer asks the authoritative DNS server for the IP address that corresponds to the domain name they’re trying to visit.
A recursive DNS server is like a helper for your computer. When your computer wants to visit a website, it asks the recursive DNS server for the IP address that corresponds to the domain name. The recursive DNS server then goes and asks the authoritative DNS server for the information. Once it gets the information, it sends it back to your computer, which can then connect to the website.
Recursive DNS servers are important because they can help to speed up your internet experience. They store information about domain names and their corresponding IP addresses in a special cache so that they can quickly give you the information you need without having to go all the way to the authoritative DNS server every time.
What are DNS records?
DNS records are like little notes that tell your computer where to find a website. They are a part of the DNS system, which helps your computer find the right website when you type in a name like “google.com".
There are different types of DNS records, each one with a different job. Here are some of the most common ones:
A (Address) record: This is the most important DNS record because it tells your computer the IP address of the web server hosting a website. When you type in a website name like “google.com", your computer looks up the A record for that domain name to find the IP address of the web server.
CNAME (Canonical Name) record: This record is like a shortcut. It tells your computer to look up the IP address for one domain name, but use the website content from another domain name. For example, the CNAME record for “test.google.com” might tell your computer to use the website content from “google.com". This record is usually used in place of an A record. All CNAME records always point to a domain, not an IP address.
MX (Mail Exchange) record: This record tells your computer where to send an email for a domain name. It’s used by email servers to find the correct destination for incoming email messages.
TXT (Text) record: This record is like a note that can contain any kind of text information. It’s often used to provide additional information about a domain name, such as ownership or security details.
These are just a few examples of the types of DNS records that exist. Each one has a specific job to help your computer find the right website or send an email to the right place. DNS records are like little helpers that work together to make sure everything on the internet runs smoothly!
What is DNS propagation and caching?
When you type in a website name like “google.com", your computer uses the DNS system to find the IP address of the web server hosting that website. But did you know that the DNS system can take some time to update with new information?
This is because of something called DNS propagation. When a change is made to the DNS records for a domain name, it can take some time for that change to be propagated, or spread out, to all of the DNS servers around the world. This means that some people might still see the old information for a little while, even after a change has been made.
Another thing to know about DNS is that your computer doesn’t always look up the DNS information from scratch every time you visit a website. Instead, it stores the information in a cache or a temporary storage area, so it can access it more quickly the next time you visit that website.
DNS caching is helpful because it makes your internet experience faster and smoother. Your computer doesn’t have to spend time looking up the DNS information every time you visit a website. Instead, it can use the information it already has stored in the cache.
However, DNS caching can also cause problems when changes are made to DNS records. Because your computer is using the cached information, it might not see the updated information right away. This is another reason why DNS propagation can take some time. You can flush the DNS cache to get rid of this issue.
So, DNS propagation and caching are two things that affect how quickly and accurately your computer can find the websites you’re looking for. Sometimes it might take a little bit of time for everything to update, but don’t worry — your computer and the DNS system are always working hard to make sure you can access the internet quickly and easily!
What are DNS security and DNSSEC?
DNS security is important because it helps to make sure that the DNS system is working correctly and that you’re truly connecting to the website you think you are. Someone could try to trick the DNS system, either by changing the DNS records for a website or by creating a fake website that looks like the real one.
One way that DNS security is improved is through something called DNSSEC. This is a system that adds extra security information to the DNS records for a website. When your computer looks up the DNS information for a website that has DNSSEC, it can check the security information to make sure that the information it’s getting is really from the website it thinks it is.
DNSSEC works by adding a digital signature to the DNS records for a website. This signature is like a special code that proves that the information is real and hasn’t been tampered with. Your computer can check the signature to make sure that it’s connecting to the real website and not a fake one.
DNSSEC is a very important part of DNS security because it helps to protect against attacks that try to trick the DNS system. With DNSSEC, you can be more confident that the websites you’re visiting are the ones you intend to visit, and that your internet experience is secure and trustworthy.
How does DNS load balancing work?
Sometimes, when lots of people want to visit a website, the server that hosts that website can get overwhelmed and stop working properly. This can make the website slow or even cause it to crash! To prevent this from happening, website owners can use something called DNS load balancing.
DNS load balancing is when a website owner sets up multiple servers to host their website. When someone tries to visit the website, the DNS system can choose which server to send them to. This helps spread out the traffic and prevent any server from getting too overwhelmed.
One way that the DNS system can choose which server to send someone to is by using something called round-robin DNS. Round-robin DNS is when the DNS system rotates through a list of IP addresses for the different servers. So, if three servers are hosting a website, the DNS system might send the first person who tries to visit the website to the first server, then send the second person to the second server, and so on.
Round-robin DNS is a simple and effective way to do DNS load balancing. By spreading out the traffic among multiple servers, website owners can ensure that their website stays fast and responsive, even when lots of people are trying to visit it simultaneously.
How do I troubleshoot DNS?
Sometimes, things can go wrong with DNS servers. When this happens, you can use the following checklist of troubleshooting techniques to use to figure out what’s going on.
Check your internet connection: Before you do anything else, make sure that your internet connection is working properly. If your internet connection is down, you won’t be able to access any websites, no matter what you do!
Try a different device: If you’re having trouble accessing a website on one device, try accessing it on a different device. This can help you figure out whether the problem is with the website or with your device.
Check your DNS settings: Make sure that your device is set up to use the correct DNS servers. If you’re not sure what the correct DNS servers are, you can try using Google’s DNS servers (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4).
Clear your DNS cache: Sometimes, your device’s DNS cache can get corrupted. When this happens, you might not be able to access certain websites. To fix this, you can try clearing your device’s DNS cache.
Check the website’s DNS records: If you’re having trouble accessing a particular website, it could be because there’s something wrong with the website’s DNS records. You can use a special tool called a DNS lookup tool to check the website’s DNS records and see if there are any problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DNS is a critical component of the internet infrastructure that enables us to access websites and services by their domain names. Understanding the hierarchy of DNS, different types of DNS servers, DNS records, and DNS security can help us manage and troubleshoot DNS effectively. Additionally, learning about DNS propagation, caching, and load balancing can improve website performance and availability.
Finally, thank you for taking the time to read my article. I tried my best to break the concepts down into simple terms. If you found my article helpful, please make to share it with your friends and colleagues.
